By Werner van Rossum
1. The paradox of “good governance”
In most giant organizations, governance is handled as an unqualified good. It alerts self-discipline, reinforces accountability, and reassures stakeholders that dangers are being managed. As uncertainty will increase, whether or not pushed by market volatility, regulatory scrutiny, or organizational change, the instinctive response is to strengthen governance moderately than query it.
But many management groups expertise a rising pressure. Choices take longer. Administration discussions shift away from trade-offs and towards validation. Motion is delayed whereas info is refined, reconciled, and reviewed repeatedly. The group seems effectively managed, however more and more sluggish, with tangible implications for value to serve and, in some instances, profitability.
This displays a broader paradox in fashionable governance. Frameworks designed to scale back threat typically find yourself constraining decision-making, not as a result of they’re overly conservative, however as a result of they quietly redefine what management means. Management turns into related to certainty. Safety of the established order turns into mistaken for worth creation.
I’ve noticed this dynamic firsthand in a big, globally distributed power firm. A powerful cultural emphasis on flawless execution in monetary reporting regularly developed into an setting the place even immaterial threat of error was handled as unacceptable. Over time, a number of layers of assessment had been added to make sure absolute accuracy in externally reported outcomes, with every layer performing primarily the identical stage of detailed validation.
What started as a prudent response to regulatory expectations slowly expanded past its unique function. Critiques multiplied not as a result of resolution high quality required them, however as a result of the group had realized to equate extra management with higher governance. Errors of negligible monetary significance had been corrected late in reporting cycles, even when the price of doing up to now exceeded any resolution or stakeholder worth created.
As a part of a subsequent transformation of how the group labored, together with my position main enterprise evaluation and reporting actions throughout Europe, Africa and the Center East, we intentionally lowered low-value validation work and eliminated redundant layers of assessment. The target was to not weaken management, however to realign effort with materials threat and resolution relevance.
Analysis on organizational decision-making has lengthy proven that as processes and oversight mechanisms accumulate, managerial consideration shifts towards defensibility moderately than selection, notably in advanced and extremely regulated environments (Harvard Enterprise Overview, 2006; Bain & Firm, 2016). Choices turn into gated not by what leaders have to act responsibly, however by what the group can show with confidence.
In environments the place uncertainty is unavoidable, that shift issues. It adjustments not solely how selections are made, however when they’re made. Delay, in lots of instances, turns into probably the most important threat of all.
This text contributes to ongoing discussions on finance governance and enterprise efficiency administration in 3 ways. First, it distinguishes monetary assertion integrity governance from resolution governance as separate management targets with basically totally different requirements of precision and rigor. Second, it explains how the buildup of controls can produce false precision and materiality blindness as predictable governance failure modes. Third, it outlines a decision-calibrated design logic for aligning management effort with materiality, belief, and resolution cadence in advanced organizations.
2. The management reflex
Controls are not often added as a result of they’re ineffective. They’re added as a result of they really feel protected.
When organizations face uncertainty, responses are typically procedural. Extra assessment layers are launched to validate assumptions. Reconciliations deepen to make sure consistency. Approval steps multiply to show oversight. Reporting variants broaden to satisfy the expectations of various stakeholders. Every measure is defensible in isolation. Over time, their cumulative impact reshapes how the group operates.
In giant transformation packages I’ve led, this sample sometimes emerged incrementally. Controls launched years earlier to handle particular audit findings, integration dangers, or one-off points had been not often eliminated as soon as the unique concern had handed. As a substitute, they turned embedded in legacy techniques and inherited processes. Groups spent growing effort reconciling and validating info that now not influenced the underlying resolution, whereas resolution home windows remained mounted.
Throughout a serious enterprise transformation, we examined monetary variance evaluation processes intimately. Moderately than beginning with present guidelines and experiences, we started by defining what a fit-for-purpose, industry-standard course of ought to appear to be. Solely then did we make deliberate decisions about the place extra rigor created real strategic benefit.
This led to a elementary shift. We explicitly distinguished between exterior monetary reporting, which requires a excessive diploma of precision, and inside stewardship, the place numbers must be materially right moderately than completely reconciled. Non-material variations had been accepted moderately than chased. Because of this, one core variance evaluation course of was redesigned from involving greater than 100 contributors globally right into a small, centered crew performing higher-level evaluation aligned to threat and resolution relevance.
Over time, governance techniques start to prioritize the safety of present worth. The emphasis shifts towards vigilance, accuracy, and defensibility. This orientation is comprehensible. Defending what already exists feels accountable and measurable. Creating new worth, in contrast, entails judgment, experimentation, and acceptance of uncertainty.
Frameworks such because the COSO Inner Management Framework, bolstered by way of Sarbanes-Oxley necessities, play a essential position in establishing minimal requirements for reliability and integrity in monetary reporting and inside management environments (COSO, 2013; U.S. Congress, 2002). These frameworks had been designed to scale back the danger of fabric misstatement and management failure. They had been by no means meant to outline how each administration resolution must be ruled, nor to require certainty earlier than motion is taken.
Issues come up when requirements designed to stop failure are prolonged past their unique function and handled as proxies for resolution readiness. In follow, this produces governance processes which can be technically sturdy, but poorly aligned to the pace and nature of the selections they’re meant to assist.
3. Danger avoidance versus threat administration
This drift towards heavier management is commonly justified within the language of threat administration. In follow, many organizations transfer nearer to threat avoidance.
The excellence is essential. Danger avoidance seeks to get rid of uncertainty earlier than motion is taken. Danger administration accepts uncertainty and manages publicity explicitly. The previous delays selections till info feels full. The latter acknowledges that completeness is never achievable and focuses as an alternative on materiality, thresholds, and possession.
The excellence will not be semantic. It basically shapes how organizations reply to uncertainty.
In lots of organizations, residual uncertainty is handled as a motive to delay moderately than as an enter to decision-making, even when that uncertainty is effectively bounded and unlikely to change the directional selection.
Modern threat frameworks emphasize that efficient threat administration doesn’t take away uncertainty, however makes it seen and actionable, notably in strategic resolution contexts (COSO, 2017). When governance techniques tilt towards avoidance, uncertainty is handled as a flaw moderately than a situation to be managed. Forecasts are refined effectively previous the purpose the place extra accuracy adjustments course, and leaders are requested to commit solely as soon as outcomes really feel defensible from each angle.
In some unspecified time in the future, governance stops being about making higher selections and turns into about avoiding blame.
The consequence is a company that turns into extremely efficient at demonstrating care, whereas turning into much less efficient at appearing in time. Worth safety quietly replaces worth creation because the dominant goal, even in contexts the place pace and judgment are essential to efficiency.
A mature governance system doesn’t faux uncertainty might be eliminated. It makes uncertainty express, bounded, and owned. To try this, it should be grounded in a transparent understanding of what accuracy really means in follow, and what stage of precision selections really require. That’s the place many governance designs start to interrupt down.
4. Searching for assurance in false precision: when governance calls for certainty that accounting can’t ship
The shift from threat administration to threat avoidance doesn’t stay summary for lengthy. In most organizations, it turns into seen in a really particular place: how monetary info is handled inside governance processes.
Many governance frameworks carry an implicit assumption that numbers should be absolutely right earlier than selections might be made. As enterprise environments turn into extra unstable, unsure, and sophisticated, tolerance for estimation narrows. Resolution boards more and more search consolation in numbers that seem extra exact, within the perception that better numerical certainty reduces the danger of error or antagonistic outcomes. Finance groups reply by reconciling extra deeply, validating extra extensively, and refining forecasts effectively past the purpose the place extra precision results in materially improved perception.
This dynamic is never described as false precision. It’s framed as rigor, self-discipline, or prudence. But it rests on a quiet fiction: that monetary numbers can, and may, attain a stage of accuracy that the underlying accounting mannequin was by no means designed to supply.
Accrual-based accounting is inherently estimate-driven. Most of the figures that underpin enterprise decision-making usually are not exact measurements, however knowledgeable judgments made underneath uncertainty. Provisions replicate probability-based expectations moderately than certainties. Impairments depend upon assumptions about future money flows and low cost charges. Depreciation allocates value over time based mostly on estimated helpful lives. Reserves symbolize assessments of probability, not identified outcomes.
This isn’t a weak point of accounting. It’s a essential design characteristic. Accrual accounting exists exactly as a result of organizations should act earlier than outcomes are absolutely identified. It allows comparability, stewardship, and decision-making in environments the place money flows unfold over time and uncertainty can’t be eradicated.
Issues come up when governance processes implicitly deny this actuality. When resolution readiness turns into tied to ever finer reconciliation of estimated numbers, organizations start to chase a stage of precision that doesn’t exist. Extra effort produces diminishing returns. Time is consumed validating assumptions that stay assumptions, no matter what number of instances they’re reviewed or reconciled.
The price of this conduct will not be restricted to effectivity. Choices stall. Alternatives slender. In aggressive environments, ready for certainty will not be a impartial selection. It’s a resolution to delay, and delay shifts benefit to these prepared to behave with bounded uncertainty.
On this setting, precision turns into performative. Numbers seem more and more precise, whereas the underlying uncertainty stays unchanged. Governance processes sign management, however resolution high quality doesn’t enhance proportionally. In lots of instances, it deteriorates, as consideration shifts from understanding ranges, drivers, and trade-offs to explaining small variances that carry little relevance for the choice at hand.
False precision is due to this fact not an accounting failure. It’s a governance failure. It displays a mismatch between what selections require and what governance techniques implicitly demand. Choices that decision for directional confidence and understanding of threat publicity are held to requirements acceptable for exterior monetary reporting, the place accuracy and consistency are important.
The consequence is predictable. Resolution boards watch for convergence that accounting can’t ship. Finance organizations dedicate scarce capability to reconciliation moderately than deep enterprise understanding and perception technology. Leaders obtain info that’s more and more detailed, but no extra well timed or actionable.
Understanding this distinction is essential. The difficulty will not be whether or not numbers are correct. The difficulty is whether or not governance frameworks are aligned with the character of the selections being made. Till organizations explicitly confront the boundaries of precision inherent in accrual accounting, governance will proceed to optimize for certainty on the expense of pace and worth creation.
That misalignment turns into most seen when organizations fail to outline materiality in decision-making contexts. That is the place false precision does the best harm.
5. Materiality blindness: when governance forgets why accuracy exists
False precision turns into most damaging when organizations lose sight of why accuracy exists within the first place.
In monetary reporting, materiality has a transparent and well-established which means. Data is taken into account materials if there’s a substantial probability that its omission or misstatement would alter the full combine of knowledge accessible to an inexpensive person. Regulatory and authorized steerage reinforces that materiality will not be a purely quantitative threshold, however a contextual judgment that considers each magnitude and nature. This definition is intentionally pragmatic. It acknowledges that not all inaccuracies matter equally, and that precision solely has worth to the extent that it influences judgment and motion (TSC Industries v. Northway, 1976; Primary Inc. v. Levinson, 1988; SEC Employees Accounting Bulletin No. 99).
Inside many organizations, nevertheless, this logic erodes as numbers transfer from exterior reporting into inside governance. Materiality thresholds are not often outlined for decision-making contexts. Because of this, the requirements acceptable for statutory reporting are implicitly utilized to administration selections, even when the selections themselves don’t require that stage of precision.
When materiality is undefined, every little thing turns into essential. Small variations set off reconciliation. Minor variances demand rationalization. Residual uncertainty is handled as a failure moderately than a characteristic of knowledgeable judgment. Governance processes lose their capability to tell apart sign from noise.
This isn’t a theoretical concern. Longstanding regulatory steerage cautions in opposition to mechanical approaches to accuracy that obscure qualitative significance and warp conduct. Materiality is explicitly meant to be assessed in context, moderately than lowered to numerical thresholds or pursued by way of repeated correction of immaterial variations. But inside governance continuously does the alternative. Finance organizations expend important effort reconciling non-material variations between plans, forecasts, and actuals, even when these variations don’t have any bearing on the choice at hand (SEC Employees Accounting Bulletin No. 99; SEC Employees Accounting Bulletin No. 108).
The results are predictable. Resolution cycles lengthen. Administration consideration shifts from option to rationalization. Leaders turn into conditioned to attend for cleaner numbers moderately than interact with ranges, sensitivities, and trade-offs.
Extra subtly, materiality blindness reinforces threat avoidance. When each quantity is handled as essential, uncertainty turns into unacceptable. Choices are deferred till obvious readability emerges, even when that readability is illusory. Governance alerts accountability, whereas the group steadily loses responsiveness.
Materiality, correctly utilized, does the alternative. It restores proportionality. It focuses effort the place it issues most. It aligns analytical rigor with resolution worth moderately than reporting conference.
The failure, due to this fact, will not be one in every of compliance. The requirements are clear. The failure lies in governance design. When organizations import reporting-grade precision into resolution contexts with out redefining materiality, they mistake accuracy for perception and management for effectiveness.
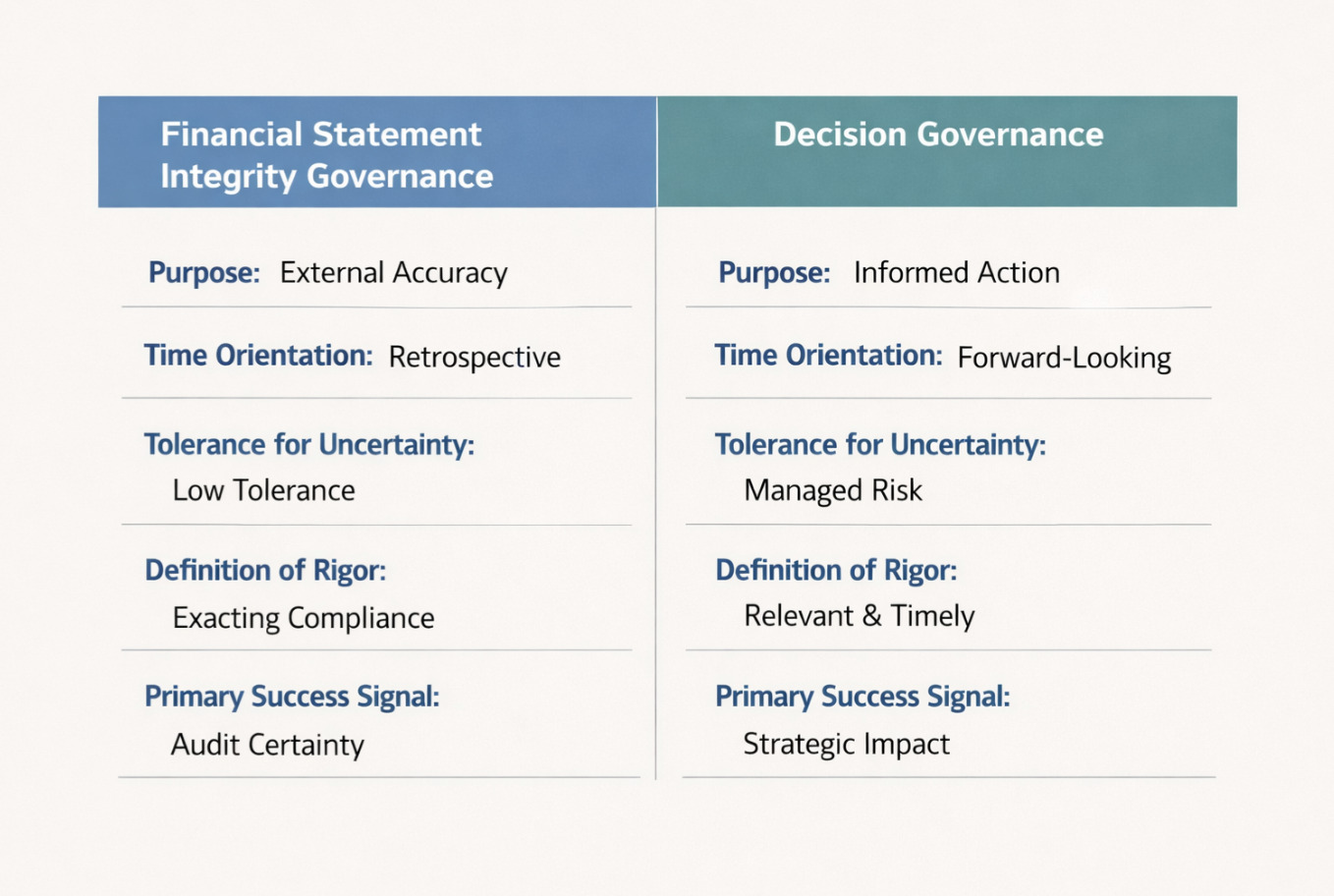
6. Resolution governance versus monetary assertion integrity governance
Many governance debates stall as a result of they assume a single governance goal. In actuality, giant organizations function underneath not less than two distinct and equally respectable types of governance, which are sometimes conflated.
The primary is monetary assertion integrity governance. Its function is to guard exterior stakeholders by guaranteeing that reported outcomes are correct, constant, and compliant with relevant requirements. This type of governance is essentially conservative, retrospective, and illiberal of error. Its rigor is non-negotiable, and its worth is evident.
The second is resolution governance. Its function is to allow well timed, well-informed administration selections underneath uncertainty in advanced and unstable environments. Resolution governance is forward-looking by design. It doesn’t search to get rid of uncertainty, however to floor it, certain it, and make it actionable.
Issues come up when these two governance targets are implicitly handled as interchangeable. Requirements designed to safeguard exterior reporting are utilized to inside decision-making. Rigor acceptable for monetary statements is imposed on analyses meant to information motion. The consequence will not be stronger governance, however slower selections and diminished worth creation.
In a big, multi-year finance and analytics transformation I led, this distinction was made express. Monetary assertion integrity governance remained unchanged, with full rigor utilized to exterior reporting. On the similar time, resolution governance was redesigned in order that planning, forecasting, and efficiency discussions had been anchored in materials thresholds aligned to govt resolution boards moderately than reporting tolerances. This separation allowed selections to maneuver sooner with out growing threat, as a result of uncertainty was surfaced and owned moderately than eradicated by way of reconciliation.
Resolution governance requires a special design logic. It asks totally different questions. What resolution is being made. What stage of accuracy is adequate to make that call responsibly. What uncertainty stays, and who owns it. What vary of outcomes is suitable given the danger and alternative profile.
On this context, rigor will not be outlined by precision alone. It’s outlined by relevance, proportionality, and timeliness. Numbers should be dependable sufficient to tell course, not flawless sufficient to fulfill reporting requirements that had been by no means meant to manipulate managerial selection. In some instances, monetary reporting accuracy is an absolute requirement. In others, accepting bounded imprecision is extra acceptable to the choice being made.
In follow, efficient resolution governance is troublesome to maintain when analytics is tightly coupled to common ledger buildings or particular person techniques of document. When each change in transactional techniques propagates instantly into resolution metrics, materiality thresholds collapse and reconciliation stress returns. Separating decision-grade analytics from underlying ledgers, typically by way of steady semantic layers, permits governance to deal with resolution relevance moderately than mechanical accuracy.
This distinction doesn’t weaken management. It strengthens it. Monetary assertion integrity governance stays important and uncompromised. Resolution governance enhances it by guaranteeing that governance frameworks assist motion in addition to assurance.
Organizations that make this distinction explicitly are capable of transfer sooner with out being reckless. They settle for bounded uncertainty the place acceptable, whereas sustaining excessive requirements the place accuracy is actually essential. Organizations that fail to make the excellence typically transfer slowly whereas believing they’re being prudent.
Reframing governance on this approach doesn’t require new techniques or looser self-discipline. It requires readability. Readability about function. Readability about materiality. And readability in regards to the distinction between governing outcomes and governing selections.
This distinction between governance targets is summarized conceptually in Determine 1.
Determine 1: Two distinct governance targets require totally different definitions of rigor, materiality, and resolution readiness.
 Conclusion: governance as an enabler of judgment, not an alternative to it
Conclusion: governance as an enabler of judgment, not an alternative to it
Governance is commonly mentioned as a constraint on decision-making. In follow, the better threat for a lot of organizations will not be too little governance, however the improper form utilized within the improper locations.
When requirements designed to guard monetary assertion integrity are prolonged wholesale into decision-making contexts, organizations drift towards false precision, materiality blindness, and threat avoidance. Accuracy turns into an finish in itself. Management turns into equated with certainty. Choices sluggish, not as a result of leaders lack braveness, however as a result of governance quietly calls for a stage of assurance that accounting and analytics had been by no means designed to supply.
The treatment will not be weaker controls or looser self-discipline. It’s clearer design.
Efficient organizations distinguish between governing outcomes and governing selections. They defend the integrity of exterior reporting with rigor and consistency, whereas permitting resolution governance to function with proportionality, express materiality, and possession of uncertainty. They acknowledge that uncertainty will not be a governance failure, however a situation of working in advanced environments.
When this distinction is made express, governance turns into an enabler moderately than an impediment. Finance and analytics shift from reconciling immaterial variations to illuminating trade-offs. Leaders are requested to not watch for certainty, however to resolve responsibly inside identified bounds. Pace improves, not as a result of requirements are lowered, however as a result of rigor is utilized the place it really adjustments outcomes.
In the end, good governance will not be about eliminating threat or perfecting numbers. It’s about creating the circumstances for sound judgment. Organizations that perceive this don’t sacrifice management to maneuver sooner. They transfer sooner as a result of their governance is designed to assist judgment and decision-making moderately than delay it.
In regards to the Creator
Werner van Rossum is a senior finance and enterprise transformation chief specializing in enterprise-scale FP&A, efficiency administration, and operating-model design. He has led giant, multi-year enterprise finance and performance-management transformations throughout globally distributed organizations, specializing in aligning processes, techniques, and capabilities to enhance resolution high quality at scale.
His work facilities on designing decision-oriented FP&A fashions that scale back complexity, strengthen governance, and allow well timed, trusted perception in extremely matrixed environments. He has held management roles spanning company finance, efficiency administration, and enterprise transformation, and repeatedly contributes views on finance transformation, resolution effectiveness, and organizational design.
Werner holds an MSc in Worldwide Enterprise and has accomplished govt training in world management and transformation. He’s based mostly in the USA.
References
- Bain & Firm (2016). The 5 Steps to Higher Choices.
- Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Fee (COSO) (2013). Inner Management Built-in Framework.
- Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Fee (COSO) (2017). Enterprise Danger Administration: Integrating with Technique and Efficiency.
- Harvard Enterprise Overview (2006). Who Has the D? How Clear Resolution Roles Improve Organizational Efficiency.
- U.S. Congress (2002). Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
- U.S. Securities and Change Fee (1999). Employees Accounting Bulletin No. 99: Materiality.
- U.S. Securities and Change Fee (2006). Employees Accounting Bulletin No. 108.
- TSC Industries, Inc. v. Northway, Inc., 426 U.S. 438 (1976).
- Primary Inc. v. Levinson, 485 U.S. 224 (1988).
Source link
#Rethinking #Governance #Balancing #Management #Pace #Belief #European #Monetary #Overview